Black borrowers and depositors face considerable challenges in accessing banking services
November 2, 2021
By Kristen Broady, Mac McComas, and Amine Ouazad
Achieving the American dream—the opportunity to succeed, to provide food and shelter for family members, education for children, hope for a better life, and freedom of opportunity— requires capital. But, in the United States, access to capital for individuals and business owners is uneven based on race. The racial wealth gap remains significant. In 2019, the median net worth of a typical white household, $188,200, was 7.8 times greater than that of a typical Black household, $24,100 (Bhutta et al., 2020). Most houses are bought with a mortgage and most businesses rely on credit to fund their expansion.
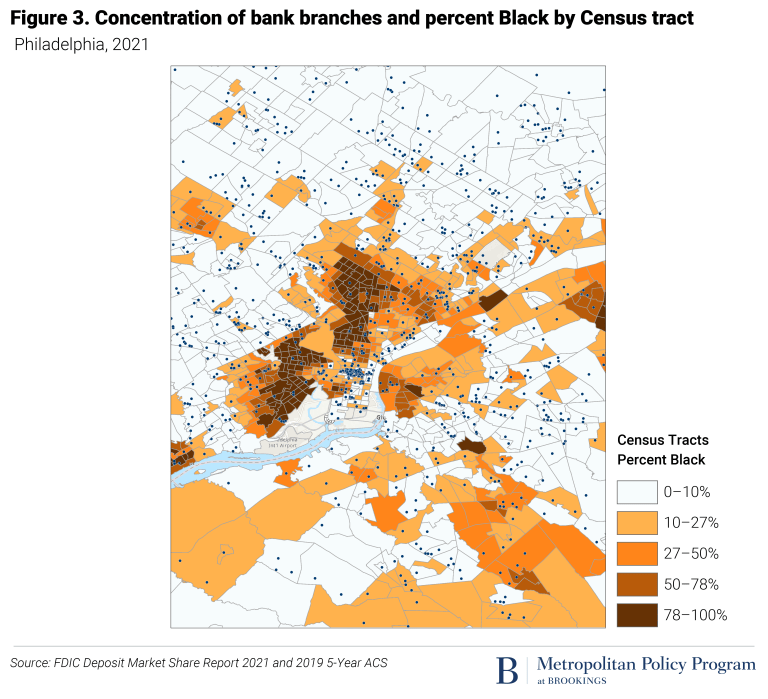
This report documents that, at a local level, there are stark contrasts in access to credit for African Americans: Interest rates on business loans, bank branch density, local banking concentration in the residential mortgage market, and the growth of local businesses are markedly different in majority Black neighborhoods. Several policy approaches are suggested: First, a more granular approach to banking supervision may be needed; microgeographic data in 2021 provides a much closer look at the banking practices of major banks and nonbank lenders than in 1977, when the Community Reinvestment Act was signed into law. Second, the number of African American minority depository institutions (MDIs) has been declining and policy or private-sector support is likely needed (Pike, 2021). Third, as the mobility of Americans is overall declining, geography matters more than ever (Molloy et al 2017). A lack of credit hinders investments in better homes, better schools, better local infrastructure such as roads and public transport, better amenities, and better health care.

